If you’ve done any type of electronics shopping recently, you’ve more than likely heard the term IP67, or some variation of it used to describe a product. IP67, and other variations, such as IP68, refer to a product’s International (Ingress) Protection Code. IP codes are used to describe a mechanical casing or electrical enclosure’s ability to protect against intrusions. These intrusions consist of body parts (such as hands and fingers), dust, and liquid (primarily water). The primary purpose of IP ratings is to give consumers more knowledge of a product’s protection. Rather than having to take the term “waterproof” at face value; with an IP rating consumers can know exactly just how waterproof an item is.
A Deeper Look
IP ratings can generally be broken down as follows:
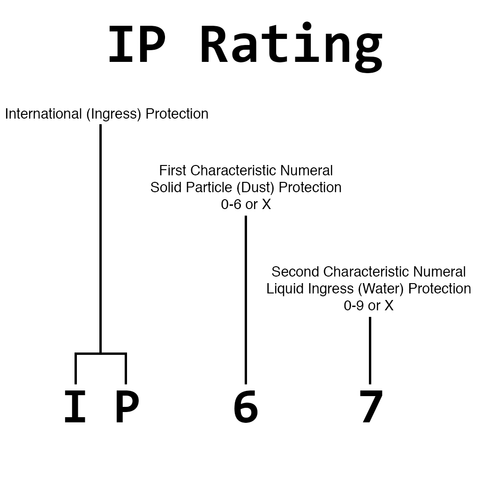
Firstly, “IP” is stated to indicate an International (Ingress) Protection Code. This is immediately followed by two mandatory numbers. The first number is used to describe the product’s solid (dust) protection. This first number can range from 0 to 6 to indicate the level of protection. However, if the product has not been tested for this type of protection, an X will be used to indicate such. The second characteristic numeral provides a product’s protection from water intrusion. This number can range from 0 to 9. Once again, an X can be used to indicate that there is insufficient data to assign a protection level.
One thing to note is that an X should not be interpreted the same as a 0, meaning no protection. Even if a product is rated IP6X for example, it does not necessarily indicate that the product is not waterproof. It simply means that the product has not been tested for liquid protection. However, that product could still very well have a high level of water protection.
While most IP ratings you come across will follow the structure shown above, IP codes can have additional letters after the two characteristic numerals. For example, ‘f’ to represent oil resistant or ‘H’ for a high voltage device.
Here is a chart of the various protection levels for reference

Examples of IP Ratings
One of the most common places you’ll find IP ratings used is in the smartphone industry. We use our smartphones almost everywhere nowadays, and I really mean everywhere (I’m looking at you shower phone users). Smartphone manufacturers are aware of this and are constantly trying to find the balance between beautiful design and protection. However, accidents will always happen, and knowing that your $1000 smartphone’s life could end after one dip in your water cup is unacceptable. Therefore, it has become almost a necessity for smartphones to have a competent IP rating to compete in today’s market.

The iPhone X and Samsung Galaxy S9 are no exceptions to this new age of standard waterproofing. The iPhone X is rated at IP67, and now that we’re IP rating experts, we as consumers can know exactly what that means. The iPhone X, according to its IP rating, can be fully immersed in water up to 1m for 30 minutes, and is completely dustproof. The Samsung Galaxy S9, however, boasts a rating of IP68. This means the S9 can be fully immersed in water up to 1.5m deep for 30 minutes, as well as being dustproof. Now, since we know the meaning of IP ratings, we see that the difference between IP67 and IP68, is not that significant, simply 0.5m. However, to the untrained eye, the difference in IP ratings could result in a deal breaker for the iPhone.
Now go forth into the world of electronics and never be fooled again!
While you’re at it, check out our Nessie Waterproof Speaker and Portable Charger

Our Nessie speaker has a rating of IPX5. Therefore, it has been tested to be quite resistant to water. It is not, however, able to be submerged completely in water. But if you’re looking for a speaker to use by the pool, at the beach, when camping, or even in the shower, the Nessie is a perfect match!








